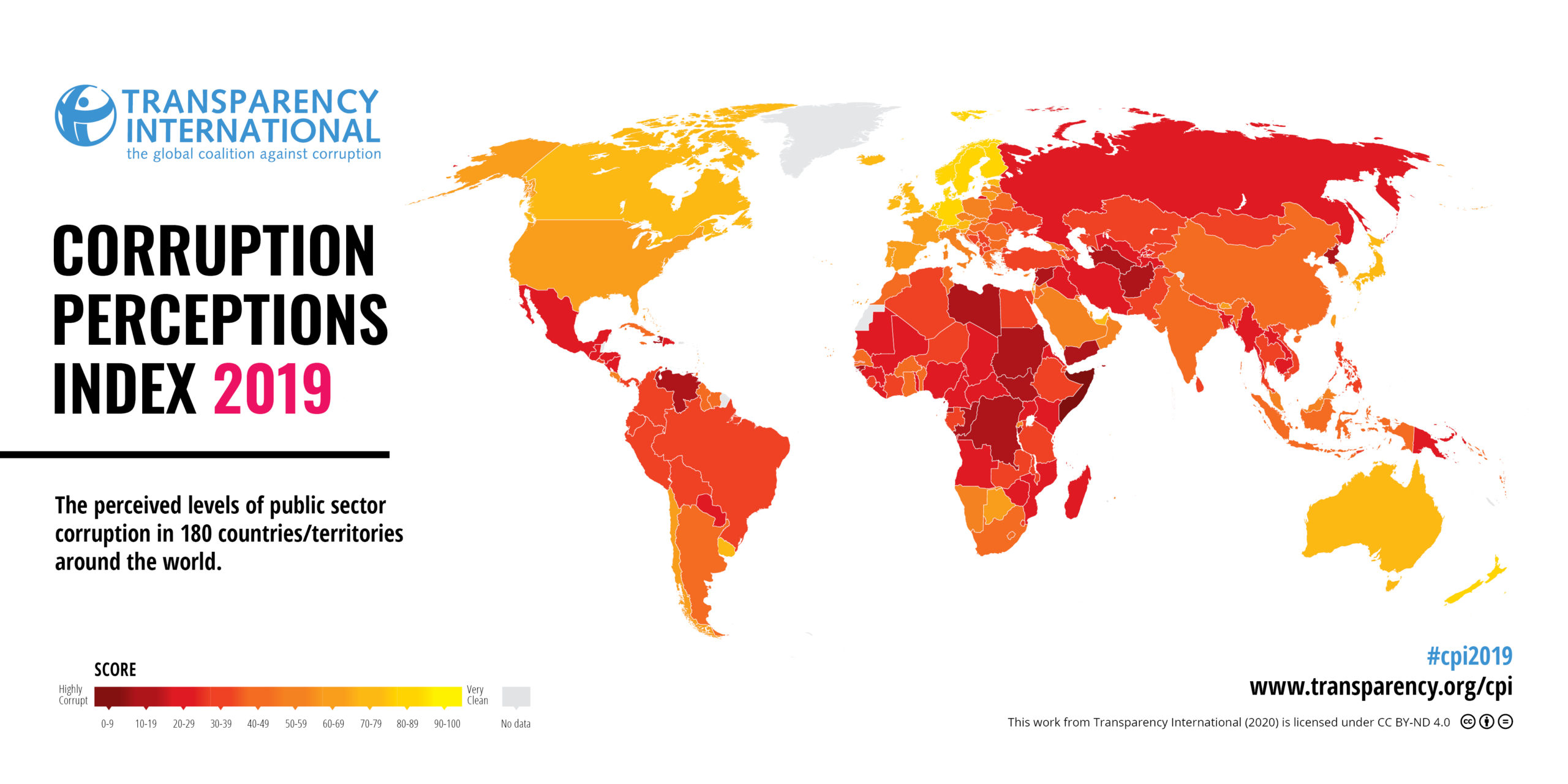
More than two-thirds of countries – along with many of the world’s most advanced economies – are stagnating or showing signs of backsliding in their anti-corruption efforts, according to the 2019 Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) released today by Transparency International. The CPI ranks 180 countries and territories by their perceived levels of public sector corruption, drawing on 13 expert assessments and surveys of business executives. It uses a scale of zero (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean). More than two-thirds of countries score below 50, with an average score of only 43. Since 2012, only 22 countries have significantly improved their scores, including Estonia, Greece and Guyana. Twenty-one have significantly declined, including Australia, Canada and Nicaragua.